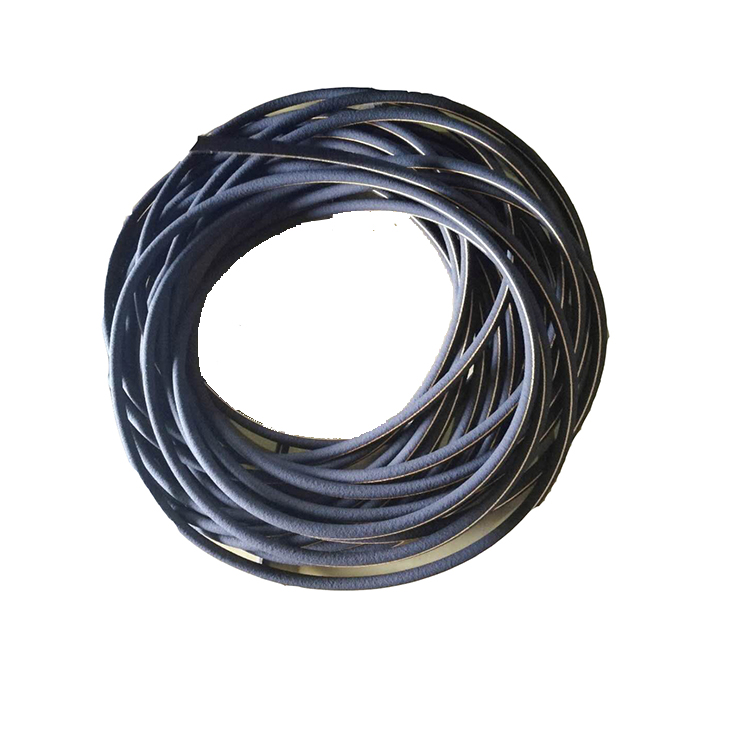
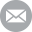
A Raschig ring is a tube of approximately equal length and diameter, used extensively as a packed bed in columns during distillation and other chemical engineering processes. They are usually ceramic, metal, or glass and provide a large surface area within the column volume for the interaction between liquid and gas vapor.
Raschig rings (especially metal Raschig rings) have many advantages:
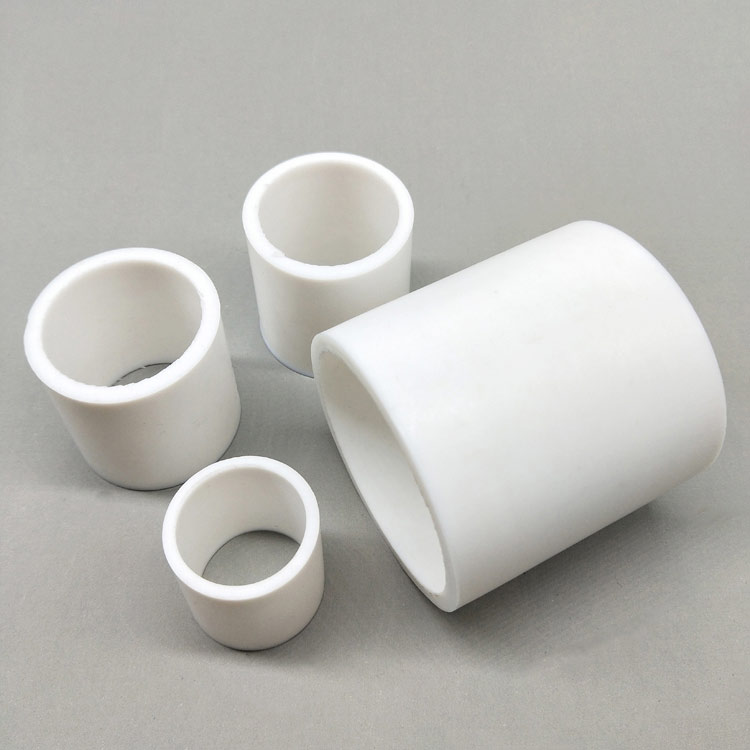

low cost. Raschig rings are made from a variety of materials and can be easily customized to the application at a low production cost.
Excellent durability. Raschig rings have a long service life due to their excellent resistance to corrosive chemicals, acids and solvents. High-strength design reduces dirt and stagnation. Additionally, they are resistant to damage caused by extreme temperatures and physical shock.
High capacity and separation efficiency. g rings have the added advantage of high capacity and separation efficiency.

Raschig Ring Use
They form what's called random packing, allowing Lacy to distill more efficiently than competitors that use fractionating columns with trays.
In a distillation column, reflux or condensed vapor flows down the column, covering the surface of the rings, while vapor from the reboiler flows up the column. When vapor and liquid pass in countercurrent in a small space, they tend to balance. Therefore, less volatile materials tend downward, while more volatile materials tend upward.
They are also used in devices where gases and liquids come into contact for gas absorption, stripping or chemical reactions, and as supports for biofilms in bioreactors.
Raschig rings made of borosilicate glass are sometimes used to handle nuclear materials. They are used in containers and tanks containing solutions of fissile material, such as concentrated uranyl nitrate solutions. They are there to act as neutron absorbers to prevent criticality accidents.